please like & Subscribe our youtube channel
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQzJncZC8PUwCTcniu_akzp0N0oDx7l1n
In this Blog, we will learn about testing, testing modules, android testing, types of testing and Monkey testing.
Android testing
From above picture, we can easily understand that testing contains with part one is JVM from java and other is the android library.
Unit Testing
In unit testing, test runs on a local JVM on the development machine rather than android runtime.
Unit testing is done by the android.jar library, all exception methods include in android.jar and execute by default.
JUnit Testing
You can use the JUnit TestCase class to do unit testing on a class that doesn't call Android APIs.
Testcase class is the super class for androidTestCase. You can easily understand with given code.
Public class Testapp extends TestCase
{
Int a;
Int b;
}
Protectd void testMethod()
{
a=10;
b=10;
}
public void testMethod () {
int c = a + b;
assertTrue(c == 5.0);
}
Monkey testing
MonkeyTalk is tools which use to test any android or I-Phone application or test and device. In android SDK include these testing tools. We can test any device or any application with two types first Junit testing and second is monkey testing. Junit test any application by test classes and the monkey is a command line tool which tests with device action like touch screen, gesture and other.
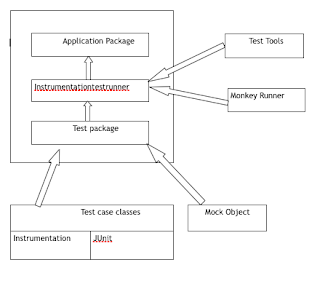
Device Testing structure
Monkey Testing Feature
There is four main feature of monkey testing.
- Basic configuration option
- Debugging option
- Event types
- Operational constraints
Monkey Testing using Shell Command for device
There are a lot of a command to execute monkey testing.
Ex: adb shell monkey -v 500
Where –v represent verbose method and 500 represents no. of the event to be sent for testing.
Monkey testing
MonkeyTalk is tools which use to test any android or I-Phone application or test and device. In android SDK include these testing tools. We can test any device or any application with two types first Junit testing and second is monkey testing. Junit test any application by test classes and the monkey is a command line tool which tests with device action like touch screen, gesture and other.
Monkey Device Testing structure
Monkey Testing Feature
There is four main feature of monkey testing.
- Basic configuration option
- Debugging option
- Event types
- Operational constraints
1) Monkey Testing using Shell Command for android device
There are a lot of a command to execute monkey testing.
Ex: adb shell monkey -v 500
Where –v represent verbose method and 500 represents no. of event to be sent for testing
2) Monkey Testing with Shell Command for android application
There are lots of commands to execute monkey testing.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> -v 500
Where -p represent package and –v represent verbose method and 500 represents no. of the event to be sent for testing.
3) Run the same event sequence again in monkey testing
Sometimes you want to check an application on the same sequence or randomly again so you will have to test exact same sequence with monkey tool.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> -s 999 –v 500
Here –s refer to seed and 999 is seed value
4) Monkey testing to get Event time
If want to set fix time between events so we can do it by the throttle.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> -- throttle 1000 –v 500
5) Monkey testing to get Touch Event percentage
We can also test an application touch event percentage.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> --pct-touch 25 –v 500
6) Monkey testing to get Motion Event percentage
We can also test an application motion event percentage.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> --pct-motion 25 –v 500
7) Monkey testing to get Any Event percentage
We can also test an application any event percentage.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> --pct-anyevent 25 –v 500
8) Monkey testing to get Number of Events
We can also find no events use on any android device.
Ex: adb shell monkey --dbg-no-event –v 500
9) Monkey testing to Ignore Crashes
If we want to fill full test an application without crashes we use this command or we want the full test by avoiding crashes. This Command avoids any type’s exception.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> –ignore-crashes –v 500
10) Monkey testing to Ignore Timeouts
If we want to fill full test an application without the timeout exception we use this command or we want the full test by avoiding timeout crashes.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> –-ignore-timeouts –v 500
11) Monkey testing to Ignore Security Exceptions
If we want to fill full test an application without security exception we use this command or we want the full test by avoiding security exception crashes.
Ex: adb shell monkey –p <package name> –-ignore-security-excetions –v 500
















No comments:
Post a Comment